| The Care and Feeding of ISDN4BSD | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| 11.1 Encapsulation Format | 11 Setting up an | 11.3 isdnd.rc Setup |
11.2 Overview
Here is an overview of the components involved in setting up ipr - based links:
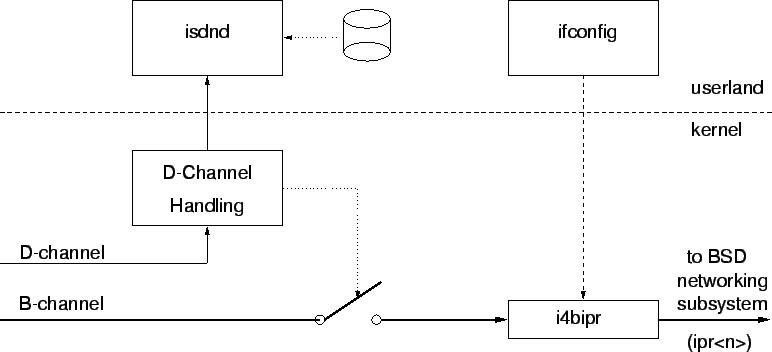
The isdn daemon isdnd has to be configured to handle the connection establishment over the D-channel. Once the connection to the remote site has been established, a B-channel is connected to the i4bipr network device driver, which basically just gets the IP packets out of the B-channel data stream and hands it to the kernels networking subsystem and vice versa. The i4bipr network device is then visible as one of the ipr<n> (for example ipr0 or ipr1) interfaces.
What does each component do?
And this is the setup for the following example:
- [isdnd]the isdn daemon is configured by its configuration database isdnd.rc. It needs at least the own and remote telephone numbers and some parameters for handling the timeout mechanism and its retry and recovery mechanisms. Isdnd is just responsible for setting up and shutting down an ISDN connection to a remote side, once a connection is active, it connects a B-channel to a driver as specified in the isdnd.rc config file and thats it. It is not involved in any data transfer on the B-channel. For more information consult the isdnd(8) and isdnd.rc(5) manual pages.
- [i4bipr]this is the network device driver which is visible (for example) as device ipr0 to the userland. As usual with network devices, the ipr<n> devices are configured by using the ifconfig command. It is required to configure the parameters address, dest_address (because this interfaces are point-to-point interfaces, a destination address is required!) and netmask (the netmask has to be 255.255.255.255 usually). Also the link0 and link1 parameters have a special meaning. For more information consult the i4bipr(4) and the ifconfig(8) manual pages.

This is my own setup for my gateway to the Internet. A dedicated Firewall machine running FreeBSD is connected to a small PBX which in turn is connected to the ISDN network of the Telekom. The remote side is a machine running the NetGW product from NetCS which is configured to use the ``IP in raw HDLC'' format.
|
|
|
|